Metallurgy is a domain of materials science that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their intermetallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are called alloys. It is also the technology of metals: the way in which science is applied to their practical use.
There are four main methods of metallurgy
STEP1.Crushing of the ore into powder.
STEP2.Concentration of the ore.
This step is done for removal of unwanted impurities from the ore.Given below are the various methods for the concentration of different ore
(a) HYDRAULLIC WASHING
(b) FROTH FLOATATION PROCESS
(c)MAGNETIC SEPARATION
(d) BAYER PROCESS(for Al)



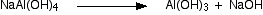

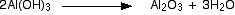
There are four main methods of metallurgy
STEP1.Crushing of the ore into powder.
STEP2.Concentration of the ore.
This step is done for removal of unwanted impurities from the ore.Given below are the various methods for the concentration of different ore
(a) HYDRAULLIC WASHING
(b) FROTH FLOATATION PROCESS
(c)MAGNETIC SEPARATION
(d) BAYER PROCESS(for Al)
Crushed bauxite is treated with moderately concentrated sodium hydroxide solution. The concentration, temperature and pressure used depend on the source of the bauxite and exactly what form of aluminium oxide it contains. Temperatures are typically from 140°C to 240°C; pressures can be up to about 35 atmospheres.
High pressures are necessary to keep the water in the sodium hydroxide solution liquid at temperatures above 100°C. The higher the temperature, the higher the pressure needed.
With hot concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, aluminium oxide reacts to give a solution of sodium tetrahydroxoaluminate
.
Impurities like iron oxide present in this ore do not react with sodium hydroxide,it is therefore separated by filtration but silica reacts to form water soluble sodium silicate.
The sodium tetrahydroxoaluminate solution is cooled, and "seeded" with some previously produced aluminium hydroxide. This provides something for the new aluminium hydroxide to precipitate around.
Aluminium oxide (sometimes known as alumina) is made by heating the aluminium hydroxide to a temperature of about 1100 - 1200°C.
STEP(3)Extraction of metal from the concentrated ore.
STEP(4)Refining or the purification of metal.
No comments:
Post a Comment