The human eye is an organ that reacts to light and has several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the mammalian eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina
allow conscious light perception and vision including color
differentiation and the perception of depth. The human eye can
distinguish about 10 million colors.
Similar to the eyes of other mammals, the human eye's non-image-forming photosensitive ganglion cells in the retina receive light signals which affect adjustment of the size of the pupil, regulation and suppression of the hormone melatonin and entrainment of the body clock.
1. vitreous body 2. ora serrata 3. ciliary muscle 4. ciliary zonules 5. Schlemm's canal 6. pupil 7. anterior chamber 8. cornea 9. iris 10. lens cortex 11. lens nucleus 12. ciliary process 13. conjunctiva 14. inferior oblique muscle 15. inferior rectus muscle 16. medial rectus muscle 17. retinal arteries and veins 18. optic disc 19. dura mater 20. central retinal artery 21. central retinal vein 22. optic nerve 23. vorticose vein 24. bulbar sheath 25. macula 26. fovea 27. sclera 28. choroid 29. superior rectus muscle 30. retina
The iris – the color of the eye – and its black center, the pupil, are seen instead of the cornea due to the cornea's transparency. To see inside the eye, an ophthalmoscope is needed, since light is not reflected out. The fundus (area opposite the pupil) shows the characteristic pale optic disk (papilla), where vessels entering the eye pass across and optic nerve fibers depart the globe.
Within these coats are the aqueous humour, the vitreous body, and the flexible lens. The aqueous humour is a clear fluid that is contained in two areas: the anterior chamber between the cornea and the iris, and the posterior chamber between the iris and the lens. The lens is suspended to the ciliary body by the suspensory ligament (Zonule of Zinn), made up of fine transparent fibers. The vitreous body is a clear jelly that is much larger than the aqueous humour present behind the lens, and the rest is bordered by the sclera, zonule, and lens. They are connected via the pupil.
As the eye ages, certain changes occur that can be attributed solely to the aging process. Most of these anatomic and physiologic processes follow a gradual decline. With aging, the quality of vision worsens due to reasons independent of diseases of the aging eye. While there are many changes of significance in the non-diseased eye, the most functionally important changes seem to be a reduction in pupil size and the loss of accommodation or focusing capability (presbyopia). The area of the pupil governs the amount of light that can reach the retina. The extent to which the pupil dilates decreases with age, leading to a substantial decrease in light received at the retina. In comparison to younger people, it is as though older persons are constantly wearing medium-density sunglasses. Therefore, for any detailed visually guided tasks on which performance varies with illumination, older persons require extra lighting. Certain ocular diseases can come from sexually transmitted diseases such as herpes and genital warts.
Similar to the eyes of other mammals, the human eye's non-image-forming photosensitive ganglion cells in the retina receive light signals which affect adjustment of the size of the pupil, regulation and suppression of the hormone melatonin and entrainment of the body clock.
1. vitreous body 2. ora serrata 3. ciliary muscle 4. ciliary zonules 5. Schlemm's canal 6. pupil 7. anterior chamber 8. cornea 9. iris 10. lens cortex 11. lens nucleus 12. ciliary process 13. conjunctiva 14. inferior oblique muscle 15. inferior rectus muscle 16. medial rectus muscle 17. retinal arteries and veins 18. optic disc 19. dura mater 20. central retinal artery 21. central retinal vein 22. optic nerve 23. vorticose vein 24. bulbar sheath 25. macula 26. fovea 27. sclera 28. choroid 29. superior rectus muscle 30. retina
General properties
The eye is not shaped like a perfect sphere, rather it is a fused two-piece unit. The smaller frontal unit, more curved, called the cornea is linked to the larger unit called the sclera. The corneal segment is typically about 8 mm (0.3 in) in radius. The sclerotic chamber constitutes the remaining five-sixths; its radius is typically about 12 mm. The cornea and sclera are connected by a ring called the limbus.The iris – the color of the eye – and its black center, the pupil, are seen instead of the cornea due to the cornea's transparency. To see inside the eye, an ophthalmoscope is needed, since light is not reflected out. The fundus (area opposite the pupil) shows the characteristic pale optic disk (papilla), where vessels entering the eye pass across and optic nerve fibers depart the globe.
Components
The eye is made up of three coats, enclosing three transparent structures. The outermost layer, known as the fibrous tunic, is composed of the cornea and sclera. The middle layer, known as the vascular tunic or uvea, consists of the choroid, ciliary body, and iris. The innermost is the retina, which gets its circulation from the vessels of the choroid as well as the retinal vessels, which can be seen in an ophthalmoscope.Within these coats are the aqueous humour, the vitreous body, and the flexible lens. The aqueous humour is a clear fluid that is contained in two areas: the anterior chamber between the cornea and the iris, and the posterior chamber between the iris and the lens. The lens is suspended to the ciliary body by the suspensory ligament (Zonule of Zinn), made up of fine transparent fibers. The vitreous body is a clear jelly that is much larger than the aqueous humour present behind the lens, and the rest is bordered by the sclera, zonule, and lens. They are connected via the pupil.
Pupil constriction
Lenses cannot refract light rays at their edges as well as they can closer to the center. The image produced by any lens is therefore somewhat blurry around the edges (spherical aberration). It can be minimized by screening out peripheral light rays and looking only at the better-focused center. In the eye, the pupil serves this purpose by constricting while the eye is focused on nearby objects. In this way the pupil has a dual purpose: to adjust the eye to variations in brightness and to reduce spherical aberration.Effects of aging
There are many diseases, disorders, and age-related changes that may affect the eyes and surrounding structures.As the eye ages, certain changes occur that can be attributed solely to the aging process. Most of these anatomic and physiologic processes follow a gradual decline. With aging, the quality of vision worsens due to reasons independent of diseases of the aging eye. While there are many changes of significance in the non-diseased eye, the most functionally important changes seem to be a reduction in pupil size and the loss of accommodation or focusing capability (presbyopia). The area of the pupil governs the amount of light that can reach the retina. The extent to which the pupil dilates decreases with age, leading to a substantial decrease in light received at the retina. In comparison to younger people, it is as though older persons are constantly wearing medium-density sunglasses. Therefore, for any detailed visually guided tasks on which performance varies with illumination, older persons require extra lighting. Certain ocular diseases can come from sexually transmitted diseases such as herpes and genital warts.



 Sodium Palmitate
Sodium Palmitate 




 ,
, and similarly the wavelength in that medium is
and similarly the wavelength in that medium is  , where
, where  is the wavelength of that light in vacuum. This implies that vacuum has a refractive index of 1, and that frequency (
is the wavelength of that light in vacuum. This implies that vacuum has a refractive index of 1, and that frequency (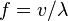 ) of the wave is not affected during refraction. Historically other reference media (e.g.,
) of the wave is not affected during refraction. Historically other reference media (e.g.,