DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - PART4
ABSORPTION OF FOOD - Absorption is the process by which the diffusible food substances pass from the lumen of alimentary tract into the blood and lymph through its mucous membrane.
PATHWAYS OF ABSORPTION - There are two pathways for absorption of food :
ABSORPTION OF FOOD - Absorption is the process by which the diffusible food substances pass from the lumen of alimentary tract into the blood and lymph through its mucous membrane.
PATHWAYS OF ABSORPTION - There are two pathways for absorption of food :
- via hepatic portal system to blood stream
Amino acids and
simple sugars →
Capillaries of mucosa
↓
Anterior mesentric
veins
↓
Hepatic Portal
Vein
↓
Hepatic Vein
↓
Inferior Vena Cava
↓
Tissue and Cells ← Blood Stream←Heart
- through lymphatic system into blood stream
Digested Food substances → Lacteals
(Products of fat digestion) ↓
Larger Lymph Vessel
↓
Main Lymph Vessel
(Thoracic duct)
↓
Blood Stream
↓
Cells and tissues
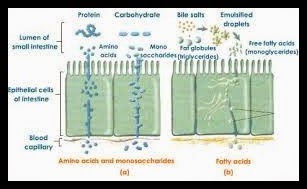
SITES OF ABSORPTION - In man, absorption mainly occurs in small intestine.
Small intestine internally bears a number of villi and microvilli to increase the surface area for absorption.Each villus contains a network of blood capillaries and a network of lymph capillaries called Lacteals.
- Very little absorption occurs in stomach of substances like water , salts, alcohol , few drugs
such as aspirin.
- A little amount of absorption also occurs in large intestine of water , vitamin B and K.
Passive absorption : In this process , substances move along concentration gradient from
place of higher concentration to that of lower concentration.No energy is required in this process.Incomplete absorption of substances occurs through this method.it takes place by physical methods as simple diffusion , osmosis and facilitated diffusion.
e.g.:Small water soluble molecules as fatty acids , monoglycerides , cholesterol and other substances are absorbed by simple diffusion.
Water is partly absorbed in small intestine and mostly in large intestine by osmosis.
Active absorption : It is brought about by specific membrane compound (carrier protein molecule) of cell membrane.
It can transport substances against their concentration gradient.It uses energy.It is a fast process and helps in complete absorption of substances.
e.g.:Nutrients like amino acids , galactose , sodium ions etc. can be absorbed only by active transport.
Absorption of fats : Short chain fatty acids and glycerol are directly absorbed into blood
stream by mucosal cells of intestine.
- Long chain fatty acids , monoglycerides , diglycerides are insoluble in water.In the lumen of intestine they combine with bile salts to form water soluble micelles.
- Micelles pass through the membrane of microvilli to enter epithelial cells.
- In epithelial cells , fatty acids , glycerol , mono and di glycerides lead to form triglycerides.
- Triglycerides , phospholipids and cholesterol combine to form chylomicrons.They enter central lacteals in intestinal villi from where they enter the venous blood through lymphatic system.
ASSIMILATION OF FOOD : Assimilation is a complex process that involves the synthesis of protoplasm (biomolecules like proteins , carbohydrates , lipids , nucleic acids etc.) in the cells from diffusible food substances brought to them by blood. It is an anabolic process.
EGESTION : It is the process of removal of undigested food substances from the alimentary
canal in the form of faeces.
DISORDERS OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM -
1.Gallstones : Gallstones are formed in the gall bladder as a result of precipitation of
cholesterol.Larger gallstones cause inflammation of gall bladder.
2.Jaundice : It is a disease in which skin and eyes look yellow due to deposits of bile
pigments .
3.Vomiting : It is ejection of stomach contents through mouth.This is a protective reflex
action which is controlled by vomiting centre in medulla.
4.Diarrhoea : The abnormal frequency of bowel movement and increased liquidity of the
faecal discharge is known as diarrhoea.
5.Constipation : Infrequent bowel movements cause constipation.In constipation, faeces
are retained within the rectum.
6. Indigestion : When food is not properly digested , a lot of gas is produced , which leads
to the distention of stomach and small intestine leading to felling of fullness.